Objective: Create an AI model to predict Copper prices#
Introduction#
The copper futures market involves the buying and selling of standardized contracts that obligate the buyer to purchase and the seller to deliver a specified quantity of copper at a predetermined price on a future date. This market allows traders and investors to speculate on the future price of copper without needing to handle the physical commodity itself. There are three of these copper futures markets in the world: Shanghai, Chicago, and London. People buy and sell these contracts based on their prediction of the future prices of these contracts. The question in this mini project is if we can build a model that can predict the price of copper contracts, specifically the one in the United States.
Methodology and Data#
In order to collect the data, we downloaded copper contract prices from three exchanges. Below is the visualization of the data:
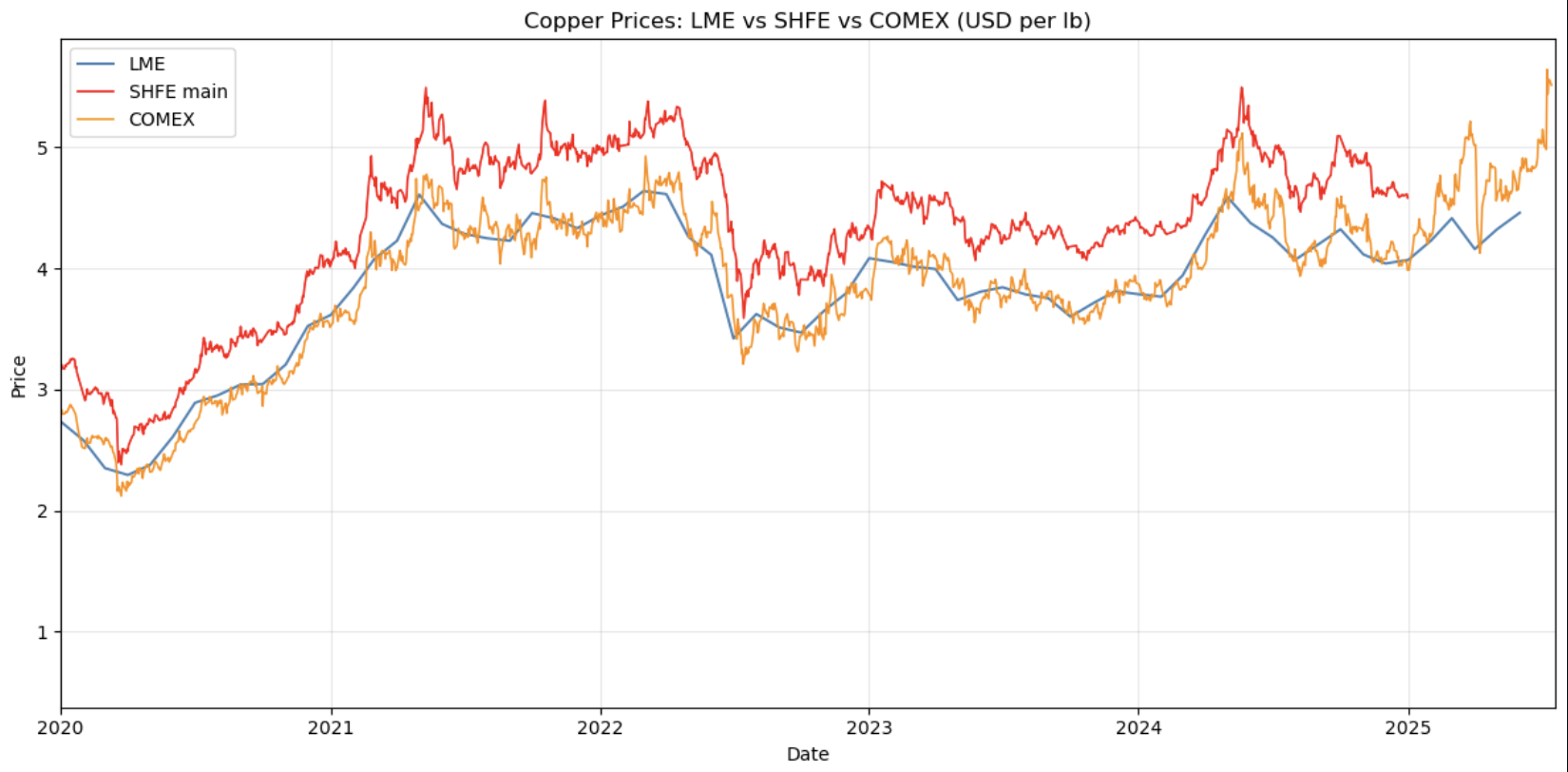
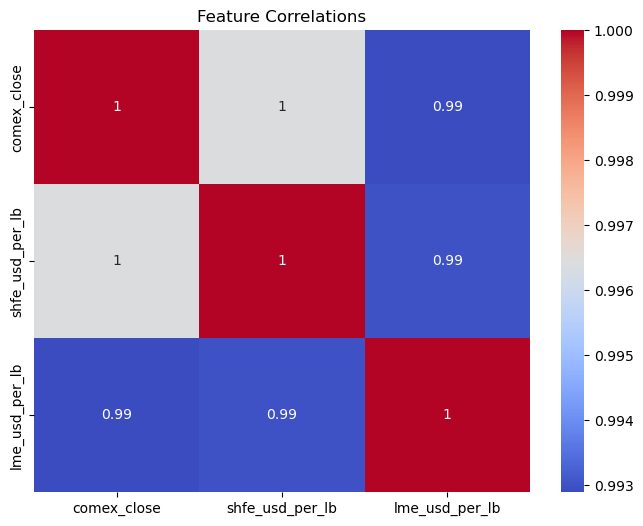
Results#
After learning more about the relationships between the three differen copper futures market, we built a Random Forest Model to predict the price of copper contracts. As a quick overview, the Random Forest Model is a model in which the model simultaneously looks at different parts of the data and combines the results of classifying similarlities and characteristics within each random sample of data. With thie model, we generated a prediction of the future values of the copper futures market. Below is our graph with the blue line representing the actual copper futures values and the orange line representing the predictted copper futures values: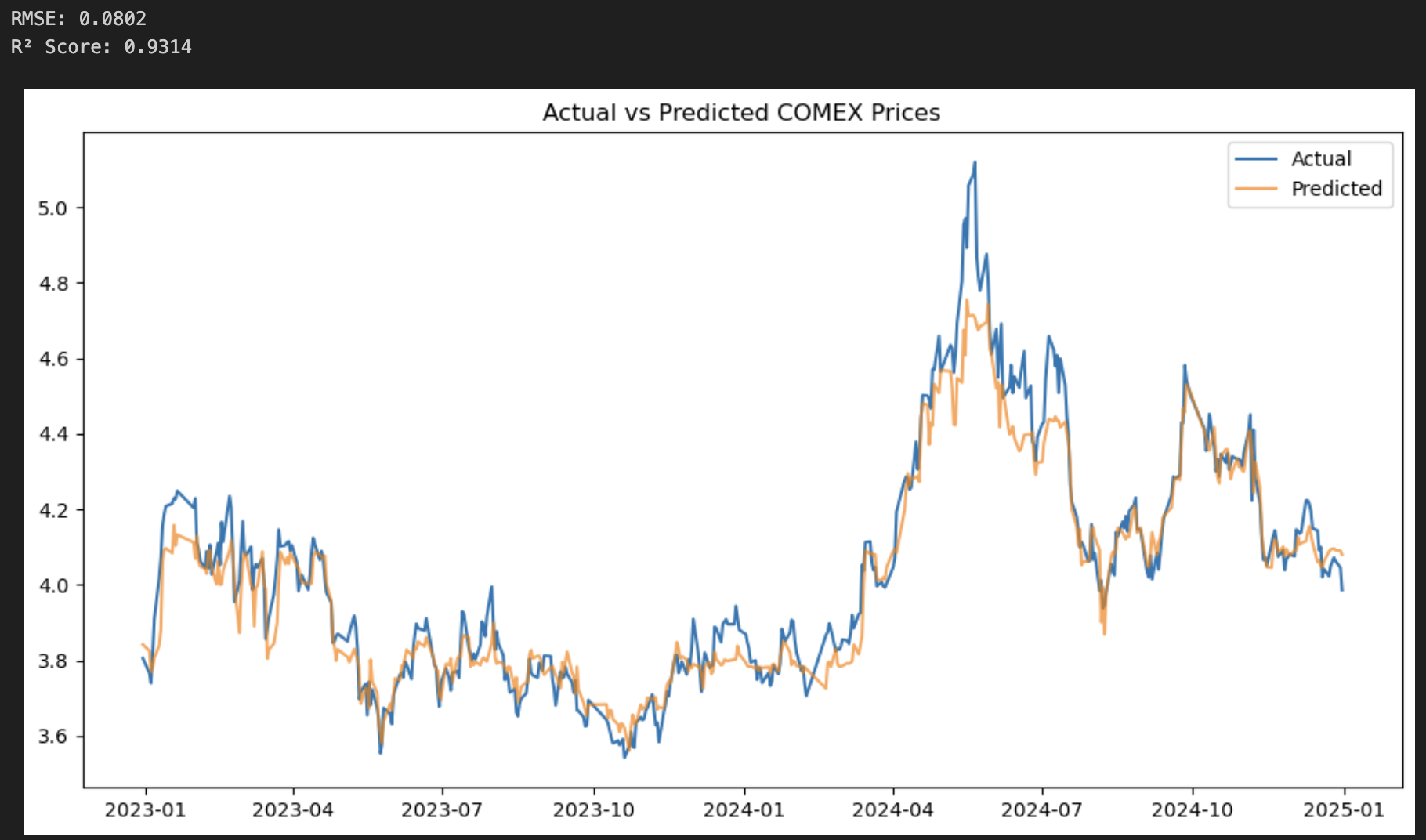
Discussion#
From the graph of the predicted vs. actual values, we can tell that our model worked quite well and was able to learn the trends of the training data and use it to predict the future values of the copper futures market. The two graphs were very close to each other, with some values a little off. The two values on the top, RMSE and R² Score, represent the differences between these two graphs. RMSE or Root Mean Square Error is obtained by calculating the differences between each points and squaring it. All the squared values are summed up in order to calculate to RMSE. The RMSE was very low, 0.0802 to be precise, meaning that our predicted graph was quite close to what the actual graph looked like. The R² Score represents the variance of the values, a 1 being that the model explains all of the variance in the dependent variable, making the model a reliant one. The R² Score for our model was 0.9314, very close to 1. Thus, our model was able to successfully capture the fluctuations and trend of the data and predict the copper futures market.
